- Eco-Friendly Product Manufacturing
- Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA)
- Fair Trade Coffee Shop
- Recycling and Upcycling
- Skill Training for Underprivileged Youth
- Socially Responsible Fashion Brand
- Mobile Healthcare Clinics
- Renewable Energy Solutions
- Community-Based Tourism
- Socially Conscious Food Truck
- Sustainable Packaging Solutions
- Microfinance Initiatives
In an era characterized by a growing emphasis on social and environmental responsibility, social enterprises have emerged as powerful solutions to address pressing global challenges.
These innovative ventures combine the entrepreneurial spirit with a deep commitment to making a positive impact on society and the planet.
By leveraging market-based strategies, social enterprises harness their resources and expertise to tackle issues such as poverty, inequality, climate change, education, and healthcare.
With their unique ability to generate both financial returns and social value, social enterprise business ideas have gained significant traction, attracting passionate entrepreneurs, investors, and consumers who seek purpose-driven solutions.
In this dynamic landscape, social enterprise stands as a beacon of hope, demonstrating that businesses can thrive while driving meaningful change.
Social Enterprise Business Ideas
Eco-Friendly Product Manufacturing
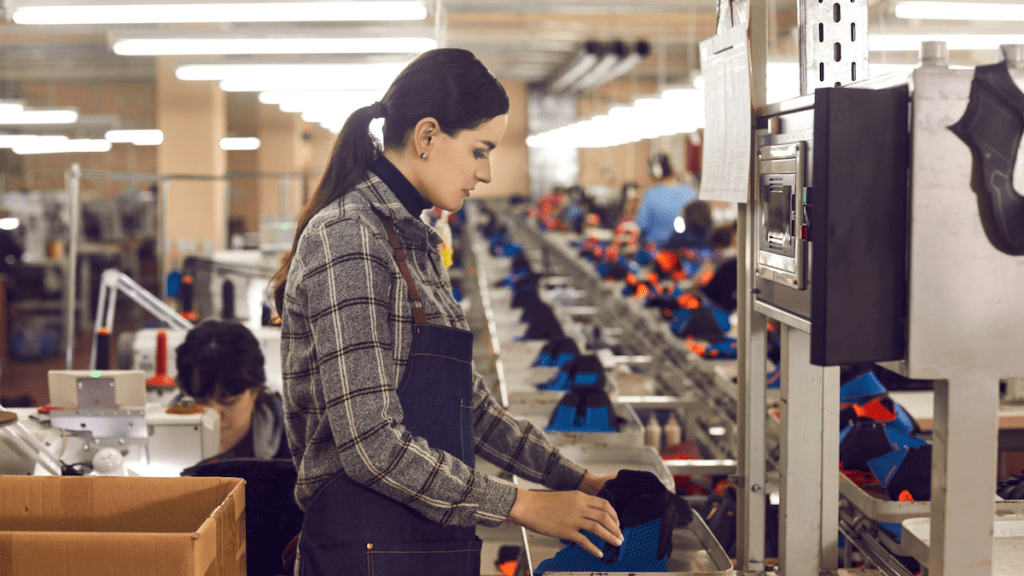

Create and sell sustainable products such as reusable bags, eco-friendly cleaning supplies, or solar-powered gadgets.
The eco-friendly product manufacturing business model centers around producing and promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly products.
It recognizes the urgent need to reduce the ecological footprint of manufacturing processes and consumer goods, aiming to minimize waste, conserve resources, and mitigate the impact on the environment.
At its core, the business model focuses on developing and manufacturing products using sustainable materials and processes.
This includes utilizing recycled, upcycled, biodegradable, renewable, and non-toxic materials as alternatives to traditional materials that have harmful environmental impacts.
The eco-friendly product manufacturing model prioritizes the use of responsibly sourced materials, such as organic fibers, sustainably harvested wood, and non-toxic dyes and coatings.
The business model also encompasses efficient and environmentally conscious manufacturing practices.
This includes optimizing production processes to minimize waste generation, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
It may involve implementing circular economy principles, such as recycling or reusing materials, and adopting eco-design approaches that consider the entire lifecycle of the product.
To sustain the eco-friendly product manufacturing business model, partnerships and collaborations are often established.
These collaborations may involve working with suppliers, research institutions, and other like-minded businesses to develop and source sustainable materials.
Additionally, partnerships with retailers and e-commerce platforms can help increase the market reach and visibility of eco-friendly products.
Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA)
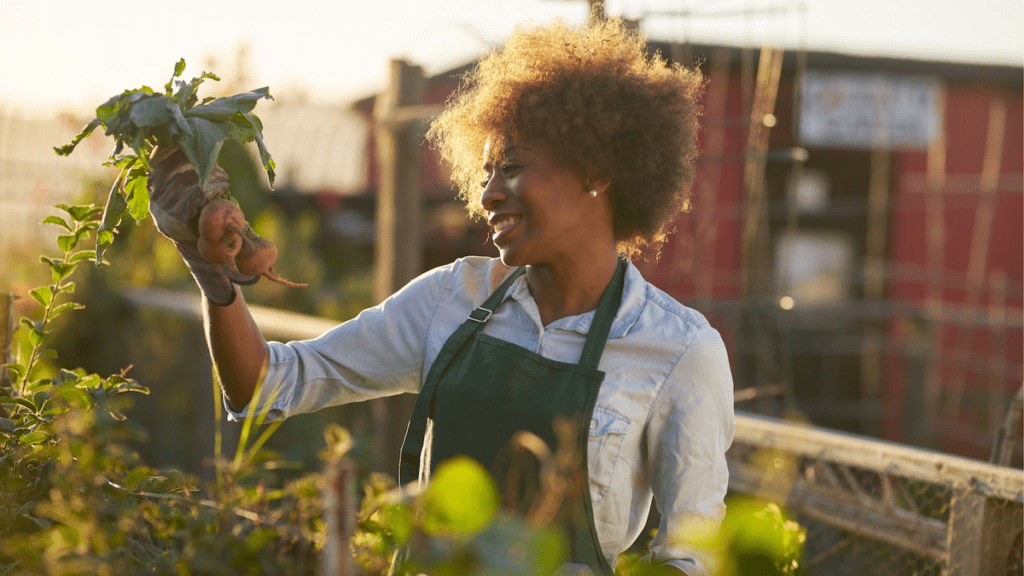

Start a farm and sell produce directly to local consumers through a subscription-based CSA model.
The Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA) business model is a unique approach to agriculture that fosters a direct connection between farmers and their local communities.
Rooted in the principles of mutual support and sustainable farming practices, CSA offers an alternative to conventional food production and distribution systems. In a CSA, members of the community become active participants in the agricultural process by purchasing shares or memberships directly from the farmer or farm cooperative.
In return, they receive a regular supply of fresh, seasonal produce throughout the growing season. This model promotes transparency, accountability, and a sense of shared responsibility, as consumers have a direct stake in the success of the farm and the quality of the food they receive.
CSA not only ensures a reliable market for farmers, but it also strengthens the local food system, promotes environmental stewardship, and builds stronger community bonds.
By supporting local agriculture and enjoying the benefits of fresh, nutritious food, CSA members actively contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food system for themselves and future generations.
Fair Trade Coffee Shop

Open a coffee shop that exclusively serves fair trade coffee, supporting small-scale farmers and promoting ethical sourcing.
The Fair Trade coffee shop business model embodies a commitment to ethical sourcing, social responsibility, and sustainable practices. Fair Trade principles ensure that coffee farmers in developing countries receive fair prices for their crops, enabling them to improve their livelihoods and invest in their communities.
In a Fair Trade coffee shop, every cup of coffee served is sourced from certified Fair Trade cooperatives or small-scale farmers who adhere to rigorous social, environmental, and economic standards.
By establishing direct relationships with these producers, Fair Trade coffee shops foster transparency and long-term partnerships based on mutual respect and trust.
Beyond sourcing, Fair Trade coffee shops prioritize creating a positive impact throughout their entire supply chain.
They emphasize environmentally friendly practices, such as using organic or shade-grown coffee beans and promoting sustainable farming methods that preserve biodiversity.
These shops also strive to provide fair and safe working conditions for their own employees, paying fair wages, offering training and development opportunities, and cultivating a supportive work environment.
By embracing the Fair Trade coffee shop model, entrepreneurs not only contribute to the well-being of coffee farmers and their communities but also tap into a growing consumer demand for ethical and socially responsible products.
These establishments serve as catalysts for change, inspiring other businesses to adopt fair trade principles and driving industry-wide transformation towards a more equitable and sustainable coffee trade.
Recycling and Upcycling
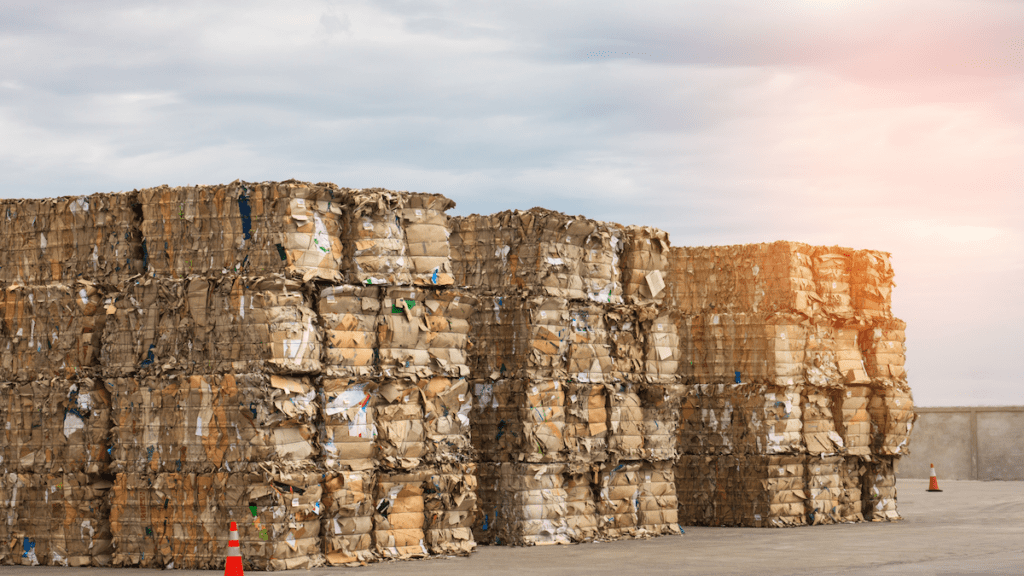

Establish a business that collects and repurposes recyclable materials or transforms waste into valuable products.
The recycling and upcycling business model champions the ideals of environmental sustainability, resource conservation, and creative innovation.
It operates on the premise that waste can be transformed into valuable resources through innovative processes and products.
Recycling involves the collection and processing of materials such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal to be reprocessed into new products.
On the other hand, upcycling takes the concept further by repurposing discarded materials into higher-value items with enhanced functionality or aesthetic appeal.
Recycling and upcycling businesses play a crucial role in diverting waste from landfills and reducing the environmental impact of production processes.
By collecting and processing recyclable materials, these businesses contribute to the conservation of natural resources, the reduction of energy consumption, and the prevention of pollution associated with the extraction and manufacturing of virgin materials.
Furthermore, by upcycling materials that would otherwise be considered waste, they encourage creativity and offer sustainable alternatives to conventional products.
Skill Training for Underprivileged Youth
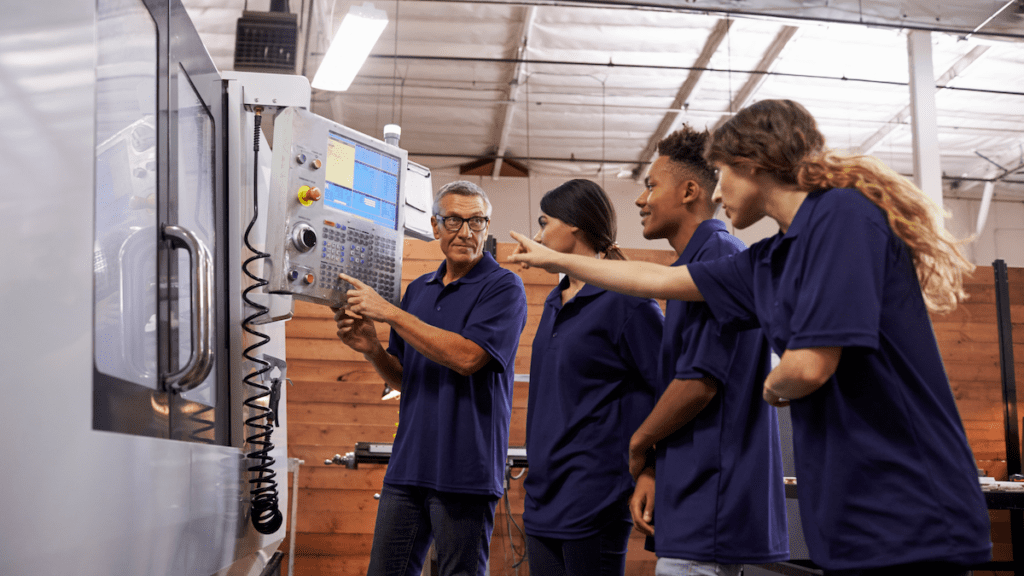

Provide vocational training and employment opportunities to disadvantaged young individuals, empowering them with marketable skills.
The Skill Training for Underprivileged Youth business model focuses on empowering and uplifting disadvantaged young individuals by providing them with essential skills and training opportunities.
This model recognizes that access to quality education and vocational training can be a transformative force in breaking the cycle of poverty and creating sustainable livelihoods.
The business model typically involves partnering with local communities, non-profit organizations, and government agencies to identify underprivileged youth who lack access to formal education or vocational training.
Through various training programs, these young individuals are equipped with practical skills and knowledge that are in demand in the job market. The training may encompass a wide range of fields such as computer literacy, technical skills, entrepreneurship, communication, and personal development.
To sustain the model, the business seeks support through grants, sponsorships, and partnerships with corporations, foundations, and government entities that share a commitment to social impact.
These collaborations provide financial resources, infrastructure, and expertise necessary for delivering effective training programs.
Additionally, the business may also explore revenue-generating avenues, such as offering fee-based training services to individuals or organizations outside the target group.
The success of this business model lies in its ability to provide not only technical skills but also comprehensive support to underprivileged youth.
This may include mentorship, career counseling, job placement assistance, and ongoing support to ensure their successful integration into the workforce.
By addressing both skill gaps and social barriers, this model aims to empower young individuals to become self-reliant, contribute to their communities, and realize their full potential.
Socially Responsible Fashion Brand

Launch a clothing line that promotes ethical manufacturing practices, fair wages, and sustainable materials.
The socially responsible fashion brand business model combines the principles of sustainability, ethical sourcing, and social impact to create a positive and transformative approach to the fashion industry.
This model recognizes the significant environmental and social challenges associated with conventional fashion practices and seeks to address them through responsible and mindful business practices.
At the core of this business model is a commitment to sustainable sourcing and production methods. Socially responsible fashion brands prioritize the use of environmentally friendly materials, such as organic cotton, recycled fabrics, and natural dyes, to minimize their ecological footprint.
They also strive to reduce waste and adopt circular economy principles by incorporating upcycling, recycling, and garment repair programs into their operations.
In addition to environmental sustainability, these brands are deeply invested in ensuring fair and ethical treatment throughout their supply chains.
They work closely with suppliers and manufacturers to ensure safe and fair working conditions for garment workers, paying fair wages, and promoting workers’ rights.
Socially responsible fashion brands often seek certifications such as Fair Trade, Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), or other recognized standards to provide transparency and accountability in their sourcing practices.
Moreover, these brands prioritize transparency and consumer education. They share the stories behind their products, highlighting the artisans, communities, and sustainable practices involved in the production process.
By fostering consumer awareness, they encourage responsible purchasing decisions and promote a shift towards conscious consumption.
To sustain this business model, socially responsible fashion brands often adopt a direct-to-consumer approach or engage in partnerships with like-minded retailers.
They may also collaborate with local artisans, cooperatives, and marginalized communities to create unique and culturally significant designs that preserve traditional craftsmanship and support local economies.
Mobile Healthcare Clinics
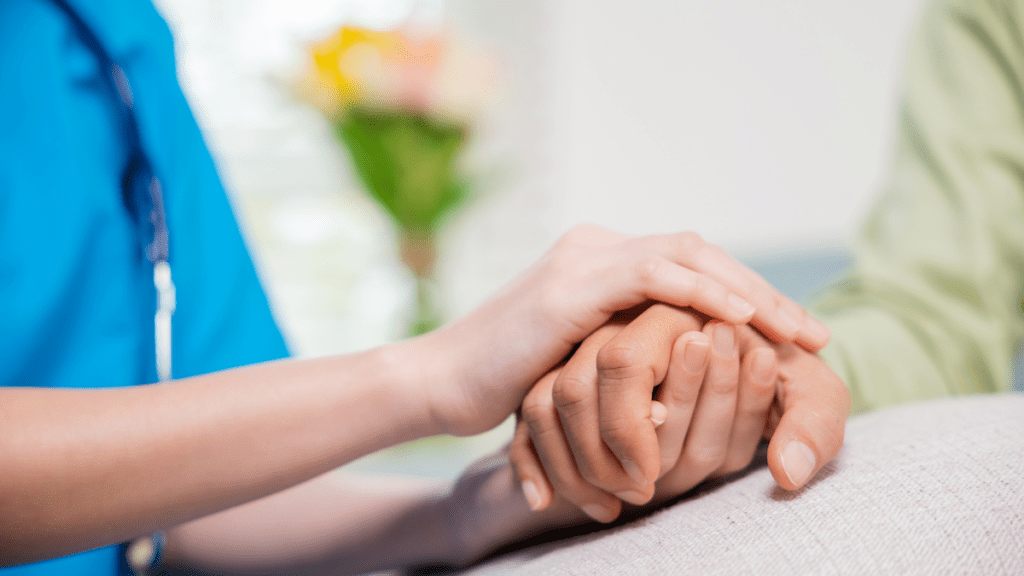

Develop mobile healthcare units that provide medical services to underserved communities, especially in remote areas.
The mobile healthcare clinics business model is a dynamic and innovative approach to delivering medical care and healthcare services directly to underserved communities.
These clinics, often housed in specially equipped vehicles, bring healthcare professionals, equipment, and resources to areas with limited access to healthcare facilities or where barriers such as transportation or distance prevent individuals from seeking timely medical attention.
The mobile healthcare clinics model aims to bridge the gap in healthcare disparities by providing comprehensive and preventive healthcare services to vulnerable populations.
These clinics are designed to be flexible and adaptable, offering a wide range of medical services such as general check-ups, vaccinations, health screenings, diagnostic tests, minor treatments, and health education.
Key components of the mobile healthcare clinics model include highly trained healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, technicians, and support staff.
These professionals provide essential medical care and education, addressing the specific healthcare needs of the target community.
The clinics are equipped with necessary medical equipment, diagnostic tools, and medications to ensure quality care is provided on-site.
To sustain the mobile healthcare clinics, partnerships with government agencies, non-profit organizations, and healthcare institutions are often forged.
These collaborations may provide funding, operational support, and access to additional resources, enabling the clinics to reach a larger number of underserved individuals.
Renewable Energy Solutions

Offer installation and maintenance services for solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy systems to reduce carbon emissions.
The Renewable Energy Solutions business model revolves around harnessing and promoting sustainable sources of energy to meet the world’s growing energy demands while reducing environmental impact.
This model recognizes the urgent need to transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and bioenergy, to combat climate change and achieve a sustainable future.
At its core, the business model focuses on developing, implementing, and managing renewable energy projects.
This includes the installation and operation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric plants, to generate clean and reliable energy.
Additionally, the model encompasses energy storage solutions to store excess renewable energy for use during periods of low generation.
The renewable energy solutions business model often involves various key components. These include technology and infrastructure development, resource assessment, project financing, regulatory compliance, and ongoing maintenance and monitoring of energy systems.
Companies operating within this model work closely with government agencies, research institutions, and investors to ensure the successful implementation and scaling of renewable energy projects.
To sustain the business model, revenue streams may come from multiple sources.
These include selling generated renewable energy to utility companies through power purchase agreements, offering energy management and consulting services, providing equipment installation and maintenance, or even engaging in energy trading within local or regional markets.
Community-Based Tourism

Organize sustainable and responsible tours that benefit local communities economically and culturally.
The Community-Based Tourism (CBT) business model centers around empowering local communities and fostering sustainable development through tourism activities.
It aims to create a mutually beneficial relationship between travelers and communities, allowing visitors to experience the local culture, traditions, and natural resources while generating economic opportunities and preserving the community’s heritage.
At the heart of the CBT business model is active community involvement and ownership.
Local residents actively participate in decision-making, planning, and management processes, ensuring that tourism activities align with their cultural values, aspirations, and environmental priorities.
By actively engaging community members, CBT promotes social inclusivity, cultural preservation, and a sense of pride and ownership over the tourism initiatives.
CBT businesses often offer a diverse range of experiences, including homestays, guided tours, cultural performances, handicraft demonstrations, and immersive activities that provide visitors with an authentic and interactive understanding of the community’s way of life.
These experiences are often designed to be small-scale, low-impact, and respectful of the environment and local traditions.
The CBT business model typically involves capacity building and training programs for community members, equipping them with the necessary skills to engage with visitors and manage tourism-related activities effectively.
This may include training in hospitality, language skills, guiding techniques, and entrepreneurship, enabling community members to take an active role in welcoming and hosting travelers.
To sustain the CBT business model, it is essential to establish partnerships and collaborations with tourism organizations, travel agencies, and government entities.
These partnerships can provide marketing support, access to wider networks, and technical assistance while ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Socially Conscious Food Truck

Operate a food truck that serves healthy, locally sourced meals, with a portion of profits supporting hunger relief programs.
The socially conscious food truck business model combines the popularity and mobility of food trucks with a deep commitment to social and environmental responsibility.
It aims to offer delicious, high-quality food while addressing pressing societal issues and promoting sustainable practices within the food industry.
At its core, the socially conscious food truck model places a strong emphasis on the sourcing and preparation of ingredients.
These food trucks prioritize local, organic, and ethically sourced ingredients, supporting local farmers and sustainable agricultural practices.
By sourcing ingredients responsibly, they aim to minimize their ecological footprint and promote the health and well-being of both consumers and the environment.
Additionally, the food truck model often incorporates social impact initiatives into its operations. This may involve partnering with local non-profit organizations or community projects to address food insecurity, support marginalized communities, or promote social causes.
For instance, some socially conscious food trucks may donate a portion of their profits to charitable organizations or implement “buy one, give one” models, where a meal is donated for each meal purchased.
Moreover, the socially conscious food truck business model actively engages with customers, fostering awareness and education about sustainable and socially responsible food practices.
Food truck operators often share information about the sourcing of ingredients, the benefits of sustainable food choices, and the impact of their social initiatives.
By engaging customers in these conversations, they aim to inspire individuals to make informed choices about their food consumption and support businesses that prioritize social and environmental well-being.
To sustain the socially conscious food truck model, collaboration and partnerships are vital. This may involve collaborations with local farmers, food cooperatives, and other socially conscious businesses to ensure a reliable supply chain of sustainable ingredients.
Additionally, working with event organizers, community festivals, and corporate clients can provide opportunities to reach a wider audience and spread their message of social consciousness.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions

Develop and sell environmentally friendly packaging alternatives, such as biodegradable or compostable materials.
The sustainable packaging solutions business model is built on the premise of providing environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional packaging materials and practices.
It recognizes the urgent need to reduce waste, conserve resources, and mitigate the environmental impact of packaging throughout its lifecycle.
At its core, the business model focuses on developing and offering sustainable packaging options that prioritize materials with lower environmental footprints. This includes utilizing recyclable, compostable, biodegradable, and renewable materials as alternatives to single-use plastics and other non-recyclable packaging options.
These materials may include bio-based plastics, paperboard, bamboo, mushroom-based packaging, and other innovative materials that are sourced responsibly and have minimal impact on the environment.
The sustainable packaging solutions business model also encompasses design and innovation. Companies within this model strive to create packaging solutions that are lightweight, space-efficient, and optimized for transportation and storage.
This minimizes the carbon footprint associated with packaging logistics and reduces waste generation throughout the supply chain.
To sustain the business model, partnerships and collaborations are crucial.
Sustainable packaging companies often work closely with product manufacturers, retailers, and e-commerce platforms to integrate sustainable packaging solutions into their operations.
This collaboration may involve providing consulting services, customized packaging designs, and supply chain management to ensure the successful implementation of sustainable packaging strategies.
Microfinance Initiatives

Create a microfinance organization that provides small loans and financial services to aspiring entrepreneurs in low-income communities, enabling them to start or expand their businesses.
The microfinance business model revolves around providing financial services to individuals and small businesses who lack access to traditional banking services.
It aims to address financial inclusion, alleviate poverty, and promote entrepreneurship by offering small loans, savings accounts, and other financial products tailored to the needs of underserved communities.
At the core of the microfinance initiatives business model is the belief in the potential and capabilities of individuals to lift themselves out of poverty given access to financial resources.
These initiatives typically target low-income individuals, marginalized groups, and micro-entrepreneurs who face barriers in accessing formal financial institutions due to lack of collateral, limited credit history, or geographical constraints.
Microfinance initiatives operate by establishing specialized financial institutions, such as microfinance banks, credit unions, or non-profit organizations.
These institutions provide small loans, often referred to as microcredit, to individuals and businesses to support income-generating activities, expand existing businesses, or cover emergency expenses.
In addition to credit, microfinance initiatives may also offer savings accounts, insurance products, and financial education to empower individuals with financial knowledge and resilience.
To sustain the microfinance initiatives business model, a combination of funding sources is typically utilized. This may include a mix of commercial investments, grants, donations, and government support.
Additionally, microfinance institutions often operate on a self-sustaining model, where the interest earned from loan repayments helps cover operational costs and further expand the reach of financial services.