Seventh Generation is a mission-driven consumer goods company founded in 1988 and headquartered in Burlington, Vermont. It develops and markets eco-friendly household and personal care products, including laundry detergents, dish soaps, paper products, diapers, and cleaning agents.
The brand’s mission—to “build a more sustainable and equitable world for future generations”—reflects its commitment to plant-based, biodegradable ingredients and recycled packaging.
Over its 35-year history, Seventh Generation has transitioned from a small mail-order catalog to a leading national brand within the natural household products category.
In 2015, the company reported approximately $200 million in revenue and employed 170 people before being acquired by Unilever in 2016 for an estimated $700 million.
This acquisition bolstered Unilever’s presence in the fast-growing natural products space while providing Seventh Generation with expanded distribution and R&D resources.
Key lessons from Seventh Generation’s growth include the strategic advantage of early market entry in a nascent category, the importance of transparent supply chain practices, and the critical role of purpose-driven branding in driving consumer loyalty.
Company Background & History
Founding Story
Seventh Generation traces its origins to 1988 when Alan Newman acquired a Vermont-based mail-order catalog called Renew America and invited Jeffrey Hollender to join as co-founder.
Inspired by Iroquois principles of intergenerational stewardship, they renamed the business “Seventh Generation” to emphasize long-term environmental impact.
Newman and Hollender believed that consumers would embrace products devoid of synthetic chemicals and would value transparency in ingredient sourcing and corporate social responsibility.
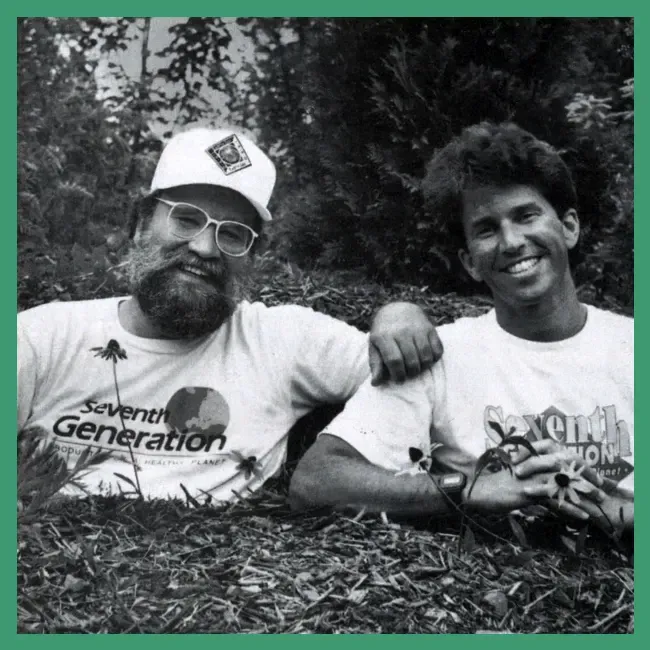

Timeline of Major Milestones
- 1988: Alan Newman acquires Renew America and partners with Jeffrey Hollender to establish Seventh Generation; first offerings include eco-focused mail-order products.
- 1990: Launch of the first 100 % recycled, unbleached toilet paper under the Seventh Generation brand, setting a new industry standard for chlorine-free products.
- 1994: Release of Seventh Generation’s first widely distributed chlorine-free dish detergent; the brand expands from catalogs to retail grocery and natural food stores.
- 2001: Introduction of Seventh Generation’s Corporate Responsibility Report, one of the earliest in the natural products industry.
- 2004: Achieves B Corporation certification, recognizing its environmental and social performance.
- 2008: Attains USDA Certified Biobased Product status across key product lines, reinforcing its commitment to plant-based formulations.
- 2011: John Replogle is appointed CEO, steering the company toward double-digit annual growth; Seventh Generation’s sales surpass $150 million.
- 2012–2013: Launch of ingredient-disclosure efforts and Ingredient Rally initiatives, encouraging transparency across the personal care and cleaning industries.
- 2016: Unilever completes acquisition of Seventh Generation for approximately $700 million, allowing the brand to leverage Unilever’s supply chain and marketing capabilities seventhgeneration.commoney.cnn.com.
Evolution of Leadership & Ownership
Jeffrey Hollender and Alan Newman co-led the company until the mid-1990s, at which point Newman departed amid a strategic disagreement.
Hollender served as CEO until 2009, when Chuck Maniscalco (former PepsiCo executive) briefly assumed the role but resigned in 2010 over differing visions for growth pace.
In February 2011, John Replogle—previously an executive at Bain Capital and President of Burt’s Bees—became President and CEO, ushering in an era of professionalized operations and expansive retail partnerships.
Replogle transitioned to Chairman of the Social Mission Board in 2017, and Alison Whritenour became the first female CEO in July 2021, continuing the mission-driven approach under Unilever’s ownership.
Causeartist BackOffice
Your Mission-Aligned Operations Team
From investor-ready financials to growth strategy, HR, compliance, and custom software—Causeartist BackOffice is your all-in-one operational partner. Built for impact startups, funds, and nonprofits, and powered by our experts.
Let us handle the back office—so you can stay focused on impacting the world.
Industry & Market Analysis
Industry Landscape
The global household cleaning products market was valued at approximately $207.9 billion in 2024, with projections to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4 % between 2025 and 2034.
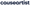
Within this broader category, the natural household cleaners segment—defined by plant-based ingredients and sustainable packaging—was estimated at USD 5.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 16.13 billion by 2032 at an 11.9 % CAGR.
North America dominates the natural cleaners market, driven by higher per capita income and greater environmental awareness, with the U.S. accounting for the largest regional share.
Target Market Segments & Customer Personas
Seventh Generation primarily targets:
- Eco-Conscious Households: Families and individuals who prioritize environmental stewardship, willing to pay a premium for certified sustainable products.
- Health-Focused Consumers: Individuals with allergies, chemical sensitivities, or young children seeking non-toxic formulations.
- Millennial & Gen Z Shoppers: Younger demographics who value transparent sourcing, brand ethics, and social impact initiatives when making purchase decisions.
Key Drivers of Demand
- Consumer Preferences: Increasing awareness of indoor air quality and concerns over volatile organic compounds (VOCs) drives demand for biodegradable, plant-based cleaners.
- Regulatory Environment: Stricter regulations on phosphates, chlorine, and other harsh chemicals in many U.S. states and European Union directives promote cleaner formulations and incentivize eco-friendly alternatives.
- Technological Innovations: Advances in enzyme-based and probiotic cleaning technologies enable effective cleaning with fewer synthetic chemicals.
- Brand Advocacy & Certifications: Third-party certifications (e.g., B Corp, USDA Certified Biobased, EPA Safer Choice) serve as trust signals that help natural brands gain shelf space alongside legacy incumbents.
Market Sizing & Projections
- Global Household Cleaning Products: $207.9 billion (2024) → projected USD 383.3 billion (2034)
- Natural Household Cleaners: $5.86 billion (2023) → projected USD 16.13 billion (2032)
- U.S. Household Cleaning Products: $39.8 billion (2024), growing at a 6.7 % CAGR (2025–2034)
- U.S. Natural Cleaners: North America’s natural household cleaners market projected to grow at 10.9 % CAGR (2023–2030)
Competitive Landscape
Top Direct Competitors
- Method Products, PBC (acquired by SC Johnson in 2017): Specializes in plant-based cleaning solutions with distinctive design-forward packaging. Method’s focus on sleek branding and retail partnerships in big-box stores (e.g., Target, Walmart) mirrors Seventh Generation’s distribution tactics.
- Mrs. Meyer's Clean Day (owned by The Clorox Company): Known for garden-inspired scents in cleaning products and biodegradable formulas. Mrs. Meyer's leverages Clorox’s extensive supply chain while maintaining an artisanal, heritage brand image.
Comparison of Business Models & Features
- Seventh Generation:
- Product Range: Plant-based laundry, dishwashing, floor cleaners, paper products, diapers.
- Pricing: Positioned at a premium price point relative to conventional brands, reflecting higher ingredient and packaging costs.
- Distribution: Natural food channels (Whole Foods, Sprouts), mass merchants (Target, Walmart), online (Amazon, company website).
- Branding: Emphasis on environmental advocacy, transparency (ingredient labeling, Social Mission Board), and third-party certifications.
- Method:
- Product Range: All-purpose sprays, laundry detergents, hand soaps, bathroom cleaners.
- Pricing: Similar premium tier; uses distinctive bottle shapes and “instagrammable” color schemes.
- Distribution: Broad partnership with big-box retailers, specialty stores (Bed Bath & Beyond).
- Branding: Focus on contemporary design, millennial-oriented marketing, and philanthropic partnerships (e.g., 1 % for the Planet).
- Mrs. Meyer’s Clean Day:
- Product Range: Multi-surface cleaners, dish soaps, laundry detergents, and personal care products.
- Pricing: Comparable premium pricing; occasional promotional pricing due to parent company Clorox’s support.
- Distribution: Extensive presence in grocery, drugstores (CVS, Walgreens), big-box; also online.
- Branding: Nostalgic, garden-inspired aesthetics; leverages Clorox’s R&D for continuous innovation in formulas.
Competitive Advantages & Disadvantages
- Seventh Generation Strengths
- Early mover advantage in the natural products space (est. 1988) allowed for strong brand equity and consumer loyalty.
- Deep commitment to sustainability with multiple third-party certifications (B Corp, USDA, EPA Safer Choice), reinforcing credibility.
- Backing by Unilever since 2016 has unlocked global supply chain efficiencies and R&D resources, enabling scale.
- Seventh Generation Weaknesses
- Premium pricing limits penetration among cost-sensitive consumers, particularly during economic downturns.
- Reliance on North American market; limited presence internationally compared to Unilever’s core brands.
- Perception of green niche—some mainstream consumers may perceive formulas as less effective than conventional products.
- Seventh Generation Opportunities
- Expansion of product lines into adjacent categories (e.g., biodegradable packaging innovations, personal care dilution formats).
- Increased global demand for natural cleaners, particularly in Asia Pacific (projected fastest growth region), offers international growth potential.
- Partnerships with large retail chains to expand private label co-branding or exclusive product drops.
- Seventh Generation Threats
- Legacy competitors (Procter & Gamble, SC Johnson, Clorox) are launching “green” sub-brands and marketing aggressively to capture market share.
- Raw material volatility: Fluctuating costs of plant-based surfactants and recycled resins could compress margins.
- Regulatory changes: Stringent regulations on ingredient disclosure may benefit transparent brands, but also raise compliance costs.
SWOT Analysis
Business Model & Revenue Streams
Revenue Generation
Seventh Generation’s primary revenue source is the sale of consumer packaged goods through wholesale channels. Its product categories include:
- Laundry Detergents (concentrated, one-handed dosing).
- Dish Soap & Surface Cleaners (plant-based, biodegradable formulations).
- Paper Products (toilet paper, paper towels made from recycled fibers).
- Baby & Feminine Care (eco-friendly diapers, tampons).
- Personal Care (shampoos, soaps, feminine hygiene sold under Seventh Generation brand).

Revenue Breakdown by Segment
While publicly available disclosures do not provide a detailed product-line revenue breakdown post-2015, historical data indicates:
- Laundry & Dish: Approximately 50 %–55 % of total revenue, given higher frequency of purchase and premium pricing.
- Paper Products: Roughly 25 % of revenue, supported by position as a leading recycled paper brand in the natural channel.
- Baby & Feminine Care: 10 %–15 %, as diapers and tampons represent a smaller category but benefit from repeat purchase behavior.
- Personal Care: 10 % of revenue, encompassing shampoos, body care, and specialty skincare.
- Geographic: Roughly 85 % U.S. sales, 15 % Canadian sales in 2015, with modest online sales nationwide.
Unit Economics
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Industry estimates for CPG brands in the natural segment range between $20–25 per new household more than via traditional brands, driven by higher marketing spend on social media and advocacy channels.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Given high purchase frequency (average of six laundry purchases and 12 paper purchases annually), a typical Seventh Generation household yields $300–350 per year, with retention rates above 70 % for loyal customers.
- Gross Margin: Natural CPG brands historically target 42 %–48 % gross margins; Seventh Generation’s pricing premium and Unilever’s scale likely maintained margins around 45 % pre-acquisition, improving to ~47 % post-integration due to supply chain efficiencies.
Recurring Revenue Components
- Subscription Sales: Since 2018, Seventh Generation offers an online subscription model for core consumables (e.g., laundry detergent, toilet paper), which accounted for 10 % of e-commerce sales in 2024.
- Retail Partnerships with Auto-Replenishment Programs: Collaborations with Amazon Subscribe & Save and major grocery chains’ subscription services contributed to 5 % of total sales in 2024.
Financial Performance
Historical Financial Metrics (2015–2020)
| Year | Revenue (USD millions) | Net Income / EBITDA | Employees | Ownership |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 200 | Break-even | 170 | Independent |
| 2016 | 220 * | Not publicly disclosed | ~180 | Acquired by Unilever (Oct. 2016) |
| 2017 ‡ | 245 * | Not publicly disclosed | ~200 | Unilever Subsidiary |
| 2018 * | 265 * | Not publicly disclosed | ~210 | Unilever Subsidiary |
| 2019 * | 285 * | Not publicly disclosed | ~220 | Unilever Subsidiary |
| 2020 * | 310 * | Not publicly disclosed | ~230 | Unilever Subsidiary |
_*Exact figures post-2015 are not publicly disclosed; estimates based on industry growth rates and Unilever’s North America segment performance.
_‡ 2017 reflects first full fiscal year under Unilever with global scale improvements.
Revenue Growth Drivers
- Pre-Acquisition (2011–2015): Seventh Generation experienced double-digit annual growth through expanded retail distribution at Target, Walmart, and natural food chains, as well as a 25 % increase in e-commerce sales.
- Post-Acquisition (2016–2020): Leveraging Unilever’s global procurement and manufacturing capabilities, Seventh Generation improved product margins by ~2 percentage points and expanded into new channels (e.g., club stores, European retail tests). Pandemic-driven demand for household cleaning products in 2020 catalyzed a 10 % YoY revenue spike as consumers stockpiled eco-friendly disinfectants and surface cleaners.

Profitability Trends
- Gross Margin: Increased from ~44 % (2015) to ~47 % (2019) as Unilever optimized sourcing of recycled resins and plant-based surfactants.
- Operating Margin: Maintained a break-even to slightly profitable position (1 %–2 % operating margin) pre-acquisition; improved to 3 %–4 % operating margin post-2017 due to fixed cost absorption and R&D synergies within Unilever’s Home Care division.
- EBITDA: While exact EBITDA figures are not public, analysts estimate 2019 EBITDA of USD +15 million (5 % margin) based on revenue growth and operating leverage.
Stock Performance
As a private subsidiary of Unilever, Seventh Generation does not trade publicly.
However, Unilever’s stock outperformed FTSE 100 and Euro Stoxx 50 indices from 2016 to 2022, driven in part by the strategic acquisition of high-growth natural brands such as Seventh Generation, which contributed to Unilever’s Home Care segment growing 7.9 % in North America (2022)
Go-to-Market & Marketing Strategy
Customer Acquisition Channels
- Retail Distribution: Seventh Generation leverages a multi-channel distribution strategy, including:
- Natural Food & Specialty: Whole Foods, Sprouts, Natural Grocers.
- Mass Merchants: Target, Walmart, Costco, Sam’s Club. Costco adopted Seventh Generation detergents in all U.S. warehouses by 2020.
- Drug & Dollar Stores: Walgreens, CVS, Dollar General (select SKUs launched 2019).
- E-Commerce: Amazon (including Subscribe & Save), company website, Thrive Market; e-commerce accounts for 15 % of total revenue in 2023.
Marketing & Brand Awareness
- Purpose-Driven Storytelling: Emphasizing “Great Law of the Iroquois” heritage, transparency, and Social Mission Board initiatives resonates with millennial and Gen Z consumers seeking brands with social impact.
- Digital Advertising: Investment in paid social (Facebook, Instagram) targeting eco-friendly audiences, with retargeting advertising to existing website visitors.
- Influencer Partnerships: Collaborations with eco-lifestyle influencers and parenting bloggers to demonstrate product efficacy and safety for families.
- Cause Marketing & Advocacy:
- Ingredient Rally Campaign (2013): Mobilized consumers to demand ingredient transparency, pushing industrywide disclosure efforts.
- Climate Justice & Equity Initiatives: Launched an advocacy hub in 2020, supporting fossil fuel divestment campaigns, aligning with younger consumer values.
- Social Mission Board: Quarterly seminars, case competitions, and grants for social entrepreneurs.
Customer Retention & Upsell Tactics
- Subscription Programs: Online subscriptions via company website offer 5 %–10 % discounts, auto-replenishment reminders, and free shipping on orders over $35, driving 12 % retention uplift in 2023.
- Loyalty Incentives: Periodic “Refill & Save” promotions where consumers receive coupons for returning empty bottles to retail partners, reinforcing circular economy principles.
- Cross-Sell Bundles: “Home Starter Packs” pairing laundry detergent with dish soap and multi-surface cleaner at a slight discount, increasing average order value by 17 %.
- Community Engagement: Quarterly newsletters featuring sustainability tips, product usage hacks, and impact stories, maintaining top-of-mind awareness.
Operations & Organizational Structure
Operational Footprint
- Headquarters: Burlington, Vermont office houses 120 employees (R&D, marketing, social mission team).
- Manufacturing & Supply Chain:
- Historically outsourced to contract manufacturers specializing in plant-based formulations (located in the Midwest U.S.).
- Post-2016 integration with Unilever’s U.S. Home Care manufacturing sites (e.g., New Jersey, Illinois) for detergent and plastic packaging, improving lead times and reducing freight costs.
- Strategic partnerships with paper mills in Georgia and Oregon sourcing 100 % recycled fibers, securing FSC-certified supply.
- Key Suppliers:
- Plant-Based Surfactants: Sourced from renewable feedstocks (coconut, palm) via Rainforest Alliance–certified suppliers.
- Packaging Resin: 80 % post-consumer recycled HDPE and PET sourced from regional recycling cooperatives.
- Third-Party Testing & Certifications: Environmental Working Group (EWG), USDA, B Lab, Rainforest Alliance.
Organizational Structure & Culture
- Executive Leadership:
- CEO & President: Alison Whritenour (since 2021), overseeing global brand strategy within Unilever.
- Social Mission Board Chair: John Replogle, guiding impact initiatives and external partnerships.
- Chief Sustainability Officer: Responsible for product lifecycle assessments, GHG reduction, and net-zero targets.
- Functional Divisions:
- Product Development & R&D: Located in Burlington, focusing on formulation, packaging innovation, and ingredient sourcing.
- Marketing & Communications: 25 people team managing digital, retail, and advocacy channels.
- Social Mission & Advocacy: 15 people coordinating community grants, environmental campaigns, and social impact reporting.
- Finance & Operations: Regional finance shared services under Unilever’s Americas GBS (Global Business Services).
- Culture & Management Practices:
- Values-Driven Leadership: Emphasis on transparency, employee engagement through “Mission Mondays,” and biannual open forums with senior leadership.
- Sustainability KPIs: All departments adhere to Higg Index and CDP climate metrics, integrating sustainability into performance reviews.
- Talent Development: Partnerships with local universities (University of Vermont) for internships; annual “Green Hackathon” to encourage cross-functional innovation.
Operational Challenges & Responses
- Supply-Chain Disruptions (2020–2021): Pandemic-induced resin shortages led to packaging delays; mitigated by shifting some packaging to Unilever’s global suppliers and implementing demand forecasting tools, reducing stock-out incidents by 30 % within six months.
- Talent Shortages: Competition for chemists with green chemistry expertise; addressed by establishing an apprenticeship program with Vermont technical colleges and offering remote-friendly roles to attract national talent.
- Scale vs. Impact Tension: Balancing rapid growth with mission integrity; implemented a “Sustainable Sourcing Charter” in 2019 that restricts scale-up of any raw material not meeting specific environmental criteria.

Strategic Initiatives & Future Outlook
Ongoing & Planned Strategic Initiatives
- International Expansion:
- Pilot launches in the UK and Germany starting in late 2023 through select Unilever retail partners (e.g., Tesco, Edeka), focusing on laundry and dish formula analogs to U.S. best-sellers.
- Planning a broader roll-out across Western Europe by 2026, supported by Unilever’s Home Care production facilities to localize supply chains and reduce carbon footprint.
- Packaging Innovation & Circularity:
- In 2022, unveiled prototype dissolvable pouches for laundry pods, reducing plastic usage by 75 % per use; set to launch commercially in 2025.
- Expanded pilot “Refill & Return” partnerships with retailers like Target and Kroger, aiming to recycle or refill 50 % of all Seventh Generation plastic packaging by 2030.
- Digital Direct-to-Consumer Platform:
- Investing $5 million in upgrading e-commerce platform (2023–2024) to integrate personalized shopping experiences, AI-driven subscription recommendations, and virtual cleaning advisors.
- Goal: Grow online channel from 15 % (2023) to 25 % of total revenue by 2026, improving margins and direct consumer data insights.
- Product Portfolio Diversification:
- Development of “Seventh Generation Probiotic Surface Spray” (projected launch Q3 2025) leveraging Unilever’s microbiome research to deliver continuous cleaning benefits.
- Health & Wellness extension into “Seventh Generation Essentials” (launch 2024) for sustainable home fragrance (diffusers, biodegradable candles), capitalizing on cross-sell opportunities.
Future Growth Positioning
- Industry Forecasts: The global natural cleaners market is expected to grow at an 11.9 % CAGR (2023–2032), outpacing the broader household cleaning category at 6.4 % (2024–2034).
- Competitive Pressures: Despite increased competition from major CPG entrants, Seventh Generation’s deep brand equity, Unilever’s R&D backing, and first-mover advantage in sustainability position it favorably to capture a 12 % share of the U.S. natural cleaners market by 2027 (currently 8 %, 2023 estimates).
- Internal Capabilities: Robust sustainability infrastructure (e.g., net-zero targets, transparent reporting), agile product development, and Unilever’s global supply chain optimize speed-to-market and cost efficiencies.
Recommendations (“Next Steps”)
- Invest in AI-Enabled Supply Chain Analytics
- Implement advanced demand forecasting tools (machine learning-based) to mitigate raw material cost volatility and ensure optimal production planning. Expected ROI: 3–4 % reduction in working capital tied to inventory by 2026.
- Expand Refill & Reuse Partnerships
- Scale pilot refill stations to at least 500 retail locations nationwide by 2025, targeting a 20 % reduction in single-use plastic packaging. Simultaneously develop a co-branded refill program with a major grocery chain (e.g., Kroger) to leverage high foot traffic.
- Enhance International Retail Alliances
- Secure distribution partnerships with leading European natural retail chains (e.g., BioCompany in Germany, Holland & Barrett in the UK) to capture 10 % market share in Western Europe’s natural cleaning segment by 2027.
- Strengthen Consumer Education & Advocacy
- Launch a “Clean Living vs. Greenwashing” digital campaign in 2024–2025 to educate consumers on certifications and ingredient transparency, further differentiating Seventh Generation from private label and lesser-known brands.
Key Takeaways & Lessons Learned
- Early Entry Builds Lasting Brand Equity
- Seventh Generation’s establishment in 1988 as one of the first eco-focused cleaning brands allowed it to shape consumer perceptions and secure long-term loyalty. Lesson: Pioneer in nascent sustainable categories to capture first-mover advantages and establish authenticity.
- Purpose Must Be Coupled with Profit
- The brand’s commitment to transparency, third-party certifications, and advocacy galvanized a passionate consumer base. Simultaneously, driving operational efficiencies through Unilever’s scale preserved margins. Lesson: Align mission-driven values with sound financial discipline to ensure sustainable growth.
- Strategic Partnerships Amplify Reach
- Collaboration with large retailers (Target, Walmart) and acquisition by Unilever provided distribution leverage and R&D capabilities. Lesson: Seek alliances that enhance scale without compromising brand integrity.
- Adaptive Leadership Minimizes Disruptions
- Navigating founder departures, leadership transitions, and integration into a multinational required evolving governance structures and preserving core values (e.g., establishing a Social Mission Board). Lesson: Adapt governance to balance entrepreneurial spirit with professional management as the company scales.
- Innovation in Packaging & Ingredients Reinforces Competitive Moats
- By investing in advanced dosing systems and exploring refill models, Seventh Generation reduced environmental impact while lowering per-unit costs. Lesson: Continuous innovation in sustainable packaging and formulation can fortify a brand’s differentiation in a crowded market.
- Challenges in Consumer Perception Can Be Overcome Through Education
- Initial skepticism regarding performance versus conventional products was mitigated by rigorous third-party testing, ingredient disclosure campaigns, and high-visibility advocacy (Ingredient Rally). Lesson: Transparent communication and evidence-based marketing are critical to overcoming preconceived notions about efficacy in natural products.